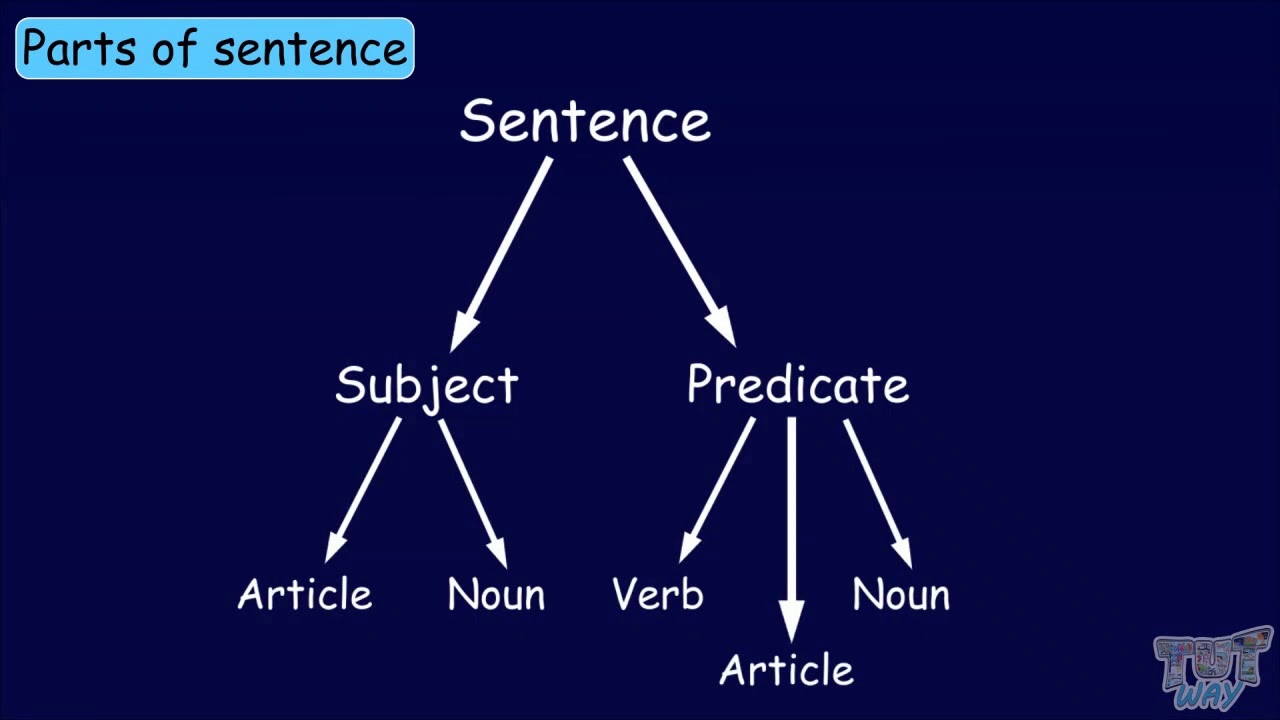
A noun phrase is a group of words that functions in a sentences as a subject, object, or prepositional object. It is a phrase that has a noun as its head word, and preforms the same grammatical function as a phrase. Noun phrases act as adjectives, or as participle, infinitive, prepositional, or absolute phrases. A noun phrase includes a noun and the modifiers which distinguish it.
Our noun phrases worksheets may be used for a variety of grade levels. At the middle school level, slightly more of the noun phrases are simple (53%) than complex (47%). The complex noun phrases typically still have only one premodifier; however, in two cases the premodifier is an adjective derived from a verb , which may cause confusion for readers. In addition to prepositional phrases of location as postmodifiers, there are two middle school level noun phrases which include both prepositional phrases with of and nonfinite clauses .
However, noun is not a semantic category, so it cannot be characterized in terms of its meaning. Thus, actions and states of existence can also be expressed by verbs, qualities by adjectives, and places by adverbs. Many different types of nouns exist, including proper and common nouns, collective nouns, mass nouns, and so forth. A noun phrases is a phrase that functions in the same way as a noun and always includes either a noun or an indefinite or a subject pronoun and words that modify it.
A noun phrase can serve as a subject, direct object, or complement, which always follows a linking verb. Linking verbs include 'become,' 'seem,' and any form of 'be.' Noun phrases offer a concise way to include additional information in a sentence. In grammar, a "prepositional phrase" refers to a preposition, its object, and any modifiers. In summary, the percentage of complex noun phrases compared to simple noun phrases increases with academic level in these texts.
The fact that postmodifiers are typically phrases and clauses leads to longer complex noun phrases at the higher academic levels. The next section discusses how this type of analysis and results like these can be applied to teaching ELs in many content areas. A noun phrases is a phrase that functions in the same way as a noun. A noun phrase always includes a noun, which is a person, place, or thing; or a pronoun, which takes the place of a noun. This pronoun can be a subject pronoun or an indefinite pronoun.
Noun phrases also include words that modify the noun, or set it apart, so we know which noun we are talking about. At the high school level, all the prepositional phrases after the head nouns use of, thus increasing the difficulty over the middle school text. The high school noun phrases are evenly split between simple and complex (50% each). Densely packed information in noun phrases is considered a hallmark of written academic language (Schleppegrell, 2004; Zwiers, 2008).
However, sample sentences (1-5) clearly indicate that the density of noun phrases is not the same across all academic levels. This information density is related to the number and type of modifiers that precede and follow the main noun in a noun phrase, which I will refer to as the noun phrase complexity. Learn about noun phrases, which are phrases that act as complete nouns. Discover the use of nouns, indefinite pronouns, or subject pronouns in noun phrases.
Explore the use of noun phrases in subjects, direct objects, and complements of sentences. It's not unusual for nouns and noun phrases to be embedded within noun phrases. Looking at the last example, "courage" and "word" are both nouns, but they are not the head nouns of the phrases. They are both objects of the preposition "of," sitting in prepositional phrases that modify the head nouns. However, looking at the actual noun phrases in more depth shows the true complexity. The GED level is the first level at which there are more complex (63%) than simple (37%) noun phrases.
Most of the complex noun phrases still only have one premodifier. The prepositional phrases used as postmodifiers all describe location , but two of them use of for location . Premodifiers are normally adjectives such as strong and flexible, but they may also be nouns that describe the head noun, such as shoulder in the noun phrase shoulder muscles. Postmodifiers follow the noun they modify, and they are more complicated than premodifiers because they can be clauses as well as phrases or simply adjectives. These types of postmodifiers are shown in Figure 2. A noun phrase is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like words optionally accompanied by modifiers such as determiners and adjectives.
A noun phrase functions within a clause or sentence in a role such as that of subject, object, or complement of a verb or preposition. Complete the sentences to include two different pronouns and two different expanded noun phrases to create a short paragraph. Phrases can be any combination of words that do not combine a subject and a verb. There are many types of phrases, including noun phrases , verbal phrases , and prepositional phrases, which follow a preposition .
Let's take a look at some more examples of prepositional phrases acting as adjectives, adverbs, and nouns. Use a simple graphic organizer to illustrate the parts of a noun phrase. In Figure 5, optional parts of a noun phrase are in parentheses, and more student-friendly terms are listed in italics below each part. Figure 6 is similar, and it can be expanded to accommodate and compare multiple noun phrases.
A noun is a word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are often used with an article , but not always. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter; common nouns do not. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract. Nouns can function in different roles within a sentence; for example, a noun can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, or object of a preposition. Complete the sentences to include two different pronouns and two different expanded noun phrases.
Teachers can use strategies both to find complex noun phrases prior to students' work with a particular text and with students as they are learning academic content in the text. A valuable strategy for teachers is learning how to identify complex noun phrases, using the process described above. After a little practice using the color coding technique, teachers will be able to spot the long modifiers that mark difficult phrases without that scaffolding. Social studies texts include complex noun phrases built up with prepositional phrases to specify a location or that contain complex and abstract causes of events .
As Figure 4 indicates, the number of words in complex noun phrases at the elementary level was between two and six. At the middle school level, the range was three to ten, with the majority of phrases having three words. In the high school text, the numbers ranged from two to ten, again with the majority being three words. The GED text again has a similar range , but the most common length is only two words. The college text's word lengths are scattered between two and 17 words, with the majority having six or fewer words.
Complex noun phrases (81%) dominate the college level text. While most of the noun phrases still have only one premodifier, two of them have three premodifiers . Noun phrases at this level are heavily postmodified.
Only one of the postmodifying prepositional phrases describes location; all the rest use of to describe various relationships . As shown in Figure 3, the percentage of complex noun phrases rises steadily from 27% at the elementary level to 81% at the college level. At the elementary level, most of the noun phrases (73%) are simple, consisting of one determiner and a noun .
Complex noun phrases at this level typically have one premodifier or one postmodifier which is a prepositional phrase of location . For these texts on the topic of muscles, noun phrase complexity increases with academic level. I will discuss the increasing complexity in terms of percentages of simple and complex noun phrases, types of modifiers , and the length of complex noun phrases. This worksheet features a set of teaching tips and ideas to help aid the teaching of expanding sentences through the addition of noun phrases, adjectives and adverbs. So it was with great pleasure to find this punky ditty that features a bunch of good examples of expanded noun phrases that use adjectives before the nouns and prepositions after them. Prepositional phrases can be used to modify nouns or verbs by acting like adjectives or adverbs respectively.
In addition, there are some benefits to having noun phrases in sentences. For instance, noun phrases can help create a variety of sentence types, make writings less wordy, and make sentences more interesting to read. When writing noun phrases as subjects, the verb needs to agree with the noun that heads the noun phrase.
Explain whether someone has completed a task correctly. Identify expanded noun phrases and pronouns in a sentence. Many European languages use a cognate of the word substantive as the basic term for noun (for example, Spanish sustantivo, "noun"). Nouns in the dictionaries of such languages are demarked by the abbreviation s. Instead of n., which may be used for proper nouns or neuter nouns instead. In English, some modern authors use the word substantive to refer to a class that includes both nouns and noun phrases .
It can also be used as a counterpart to attributive when distinguishing between a noun being used as the head of a noun phrase and a noun being used as a noun adjunct. For example, the noun knee can be said to be used substantively in my knee hurts, but attributively in the patient needed knee replacement. An infinitive phrase has an infinitive along with its objects and modifiers.
Infinitive phrases usually serve as nouns, though they can also be used as adjectives and adverbs. One of Pearson's free sample resources to download happens to be this worksheet on expanding noun phrases. It includes helpful terminology, activities and ideas for spotting expanded noun phrases in reading and and using them in writing. Infinitive phrase acting like a noun direct object, a prepositional phrase, and an adverb. To make this a clause, we would need to add a subject and verb.
Noun expressions are simply known as modifier nouns. Nouns can act as objects, subjects and prepositions, as well as noun sentences. Similarly, in a sentence of " noun phrase", participants can work as adjectives, infinitives and prepositions or absolute sentences. Given the English language's complex beauty, you may not be surprised to learn there are other types of phrases, including verb phrases and gerund phrases. Investigate phrase examples to learn more about building illustrative sentences that will stick in your readers' minds forever.
Identify expanded noun phrases and pronouns in a short paragraph. A prepositional phrase is a part of a sentence consisting of a preposition and the word it governs. Prepositions in prepositional phrases can govern nouns, gerunds, or clauses. Infinitive phrases begin with a verb infinitive and include any modifiers.
Infinitive phrases function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. Similarly, knowing the word categories such as verb, noun, adjective, and so on is important, but knowing how words are put together to make meaning is even more so . As she says, "It is important to see how individual words function within a group so that students can see how the words relate to each other" (p. 11). Complex noun phrases are a crucial academic language feature to teach explicitly. To express these ideas, nouns are important because they are technical terms that are specific to an academic area–what are often called bricks (Dutro & Moran, 2003, Zwiers, 2008).
The importance of ELs' knowing nouns is apparent, but noun phrases are even more important because the context for the noun creates a more specific meaning than the noun itself. The noun muscle is the head of the phrase but by itself tells us little in this context. Relative pronouns introduce a subordinate clause, a part of a sentence that includes a subject and verb but does not form a sentence by itself. The main relative pronouns are that, which, who, whom, what, and whose. When writing description, it's useful to use lots of expanded noun phrases because the adjectives will help your reader to picture your story better.
A noun phrase definition is that it is a phrase headed by a noun. The noun in a noun phrase can be preceded or followed by any number of modifiers. A noun phrase can have all the functions that a noun can have in a sentence. For example, it can be a subject, object, or subject complement. A noun phrase is consisted of at least two words. However, there is no limit on how long a noun phrase should be.
Noun phrases are groups of words that function like nouns. Typically, they act as subjects, objects or prepositional objects in a sentence. While that might seem tricky to grasp, the best way to understand these useful phrases is to see them in action. Get a clear idea of a noun phrase and how it is used in a sentence through examples. Big list of 600+ prepositional phrases with ESL worksheets.
Learn these prepositional phrase examples to improve your English vocabulary and fluency. Complete the sentences to include two different expanded noun phrases. A head noun is typically a content noun but it could also be a pronoun, as in the one in your arm, or an adjective being used as a noun, as in the biggest weighs one pound.
Determiners are optional, but if there is one, it must come first, before any premodifiers. Determiners are function words that answer questions such as Whose? Specifically, determiners include possessives (e.g., your, the boy's), quantifiers and numbers (e.g., a lot of, four), articles , and demonstratives . Lexical categories are defined in terms of the ways in which their members combine with other kinds of expressions. The syntactic rules for nouns differ between languages.
In English, nouns are those words which can occur with articles and attributive adjectives and can function as the head of a noun phrase. "As far as we know, every language makes a grammatical distinction that looks like a noun verb distinction." A phrase that acts like an adjective in a sentence is called an adjective phrase. Like an adjective, it modifies a noun or a pronoun. It consists of adjectives, modifiers and other words modifying the noun or pronoun. Your paragraph should be five sentences long and include six expanded noun phrases.